How to Transport Fish
Transporting fish requires careful planning and execution to ensure fish health․ Proper techniques help maintain optimal conditions for aquatic life during their journey․
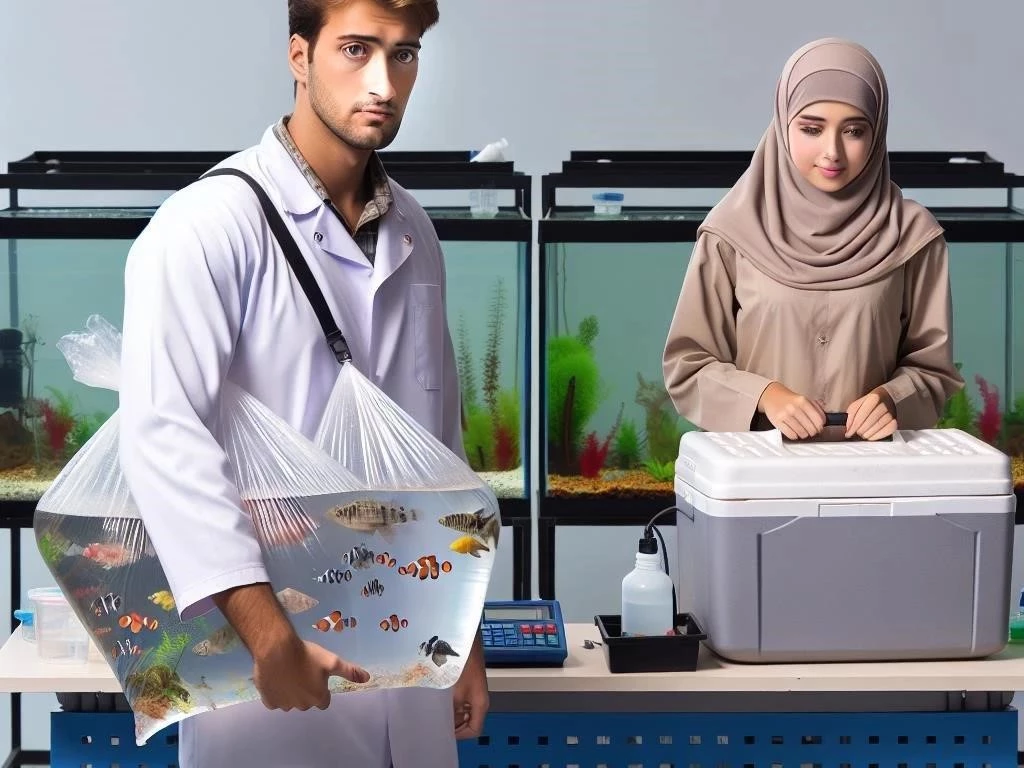
Transporting fish is a critical process that involves various methods to ensure the safety and well-being of aquatic life․ Effective fish shipping requires knowledge of fish care, including the selection of appropriate fish bags and insulated containers․ Proper handling during transport is essential for maintaining water temperature and oxygen supply, which directly affects fish health․ Understanding the travel conditions helps reduce stress and supports fish acclimation once they reach their destination․ By following best practices, fish survival rates can significantly improve, ensuring the welfare of these delicate creatures throughout their journey․
Importance of Fish Care During Transport
Fish care during transport is crucial for ensuring the health and welfare of aquatic life․ Proper handling techniques minimize stress and facilitate a smoother transition for fish․ Maintaining optimal water temperature and oxygen supply is essential, as fluctuations can lead to distress or even mortality․ Additionally, using suitable fish bags and insulated containers contributes to creating a stable environment․ By prioritizing fish care, transporters can enhance fish survival rates and promote successful acclimation post-transport․ Ultimately, responsible practices during fish shipping reflect a commitment to the well-being of these delicate creatures․
Preparing for Fish Shipping
Preparing for fish shipping involves several key steps to ensure a successful transport experience․ First, assess the specific needs of the fish species, including water temperature and oxygen requirements․ Next, select appropriate transportation methods that align with travel conditions and distance․ It is essential to gather high-quality fish bags and insulated containers to protect aquatic life during transit․ Additionally, plan the packing process meticulously to avoid overcrowding, which can compromise fish health․ Proper preparation ensures a smooth journey, ultimately enhancing the chances of fish survival during shipping․
3․1 Choosing the Right Transportation Methods
Selecting the appropriate transportation methods is vital for the successful shipping of fish․ Various options are available, including ground, air, and sea transport, each with distinct advantages․ Ground transport is often economical for shorter distances, while air transport is faster, suitable for long distances, and minimizes stress․ Consider the specific requirements of the fish species, such as temperature control and oxygen supply․ Evaluate the duration of travel and potential delays to ensure fish welfare․ Ultimately, the right transportation method supports sustainable practices and enhances fish survival rates during shipping․
3․2 Selecting Insulated Containers for Optimal Conditions
Choosing the right insulated containers is essential for maintaining optimal conditions during fish transport․ These containers help regulate water temperature and protect fish from external environmental fluctuations․ Look for sturdy, high-quality materials that provide efficient insulation and minimize heat transfer․ Ensure containers are appropriately sized to prevent overcrowding while allowing enough space for fish movement․ Additionally, verify that they are watertight to prevent leaks․ Using proper insulation reduces stress on fish and promotes their health and welfare, significantly improving survival rates during shipping and transport․
Understanding Water Temperature
Water temperature plays a critical role in the successful transport of fish, impacting their health and survival․ Different fish species thrive at specific temperature ranges, making it essential to understand these requirements before shipping․ Maintaining a stable temperature throughout the journey reduces stress and minimizes the risk of shock․ Additionally, fluctuations can lead to increased metabolism and oxygen consumption, jeopardizing fish welfare․ Employing insulated containers and monitoring temperature closely are vital strategies for ensuring an optimal environment․ Ultimately, managing water temperature effectively enhances fish survival during transport and supports their overall health․
4․1 Ideal Temperature Ranges for Different Fish Species
Understanding the ideal temperature ranges for various fish species is crucial for successful transport; Tropical fish generally thrive between 75°F to 80°F (24°C to 27°C), while temperate species prefer cooler conditions, typically around 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 21°C)․ Cold-water species, such as trout, require even lower temperatures, ideally between 50°F to 60°F (10°C to 15°C)․ Researching the specific needs of the fish being transported ensures optimal conditions, reducing stress and enhancing survival rates․ Maintaining appropriate temperatures contributes significantly to the overall fish health during their journey․
4․2 Monitoring Temperature During Transport
Monitoring temperature during fish transport is essential to ensure optimal conditions throughout the journey․ Use reliable thermometers that can provide accurate readings, and consider digital options for real-time monitoring․ Regularly check the temperature inside insulated containers to detect any fluctuations․ If necessary, use heat packs or ice packs to maintain stable temperatures, depending on the specific needs of the fish species․ Keeping a log of temperature readings can help identify trends and potential issues․ Proactive temperature management ultimately enhances fish health and survival rates during transport, reducing stress significantly․
Oxygen Supply Considerations
Ensuring an adequate oxygen supply is critical for the successful transport of fish․ As fish are transported, they continuously consume oxygen, which can quickly deplete in confined spaces․ To maintain optimal oxygen levels, use well-oxygenated water in fish bags before sealing․ Additionally, consider using oxygen-infused bags for longer journeys, which provide a more stable oxygen supply․ Regularly monitoring the conditions within containers can help assess the need for additional oxygen․ Proper management of oxygen supply significantly contributes to reducing stress and promoting fish health during transport, enhancing overall survival rates․
5․1 Ensuring Adequate Oxygen Levels in Fish Bags
To ensure adequate oxygen levels in fish bags, start by filling them with well-aerated water․ The right water volume is crucial; avoid overfilling to allow fish room to move and breathe․ Consider using oxygen tablets or a portable oxygen pump to enhance oxygenation before sealing the bags․ It’s also essential to minimize handling stress during the packing process, as this can increase oxygen consumption․ Regularly check the bags for leaks or signs of distress․ Proper management of oxygen levels is vital for sustaining fish health during transport, ultimately improving survival rates․
5․2 Using Oxygen-Infused Bags for Long-Distance Transport
Using oxygen-infused bags is an excellent strategy for long-distance transport of fish, as they provide a stable oxygen supply․ These specialized bags are filled with pure oxygen, significantly enhancing the aquatic environment for fish․ When preparing for transport, ensure that the bags are properly sealed to prevent leaks and maintain oxygen levels․ Additionally, consider the duration of the journey, as oxygen-infused bags can sustain fish health over extended periods․ This method minimizes stress and promotes fish welfare, ultimately increasing survival rates during long-distance shipping and transport․
Packing Fish for Safe Travel
Packing fish securely for safe travel is vital to ensure their well-being during transport․ Start by selecting high-quality fish bags that are durable and appropriately sized for the species․ Fill the bags with treated and well-oxygenated water, leaving enough air space for fish to breathe․ Use cushioning materials within insulated containers to minimize movement and impact during transit․ Avoid overcrowding, as this can lead to stress and health issues․ Proper packing techniques help maintain stable conditions, ultimately enhancing fish survival rates and promoting their overall health during the journey․
6․1 Using Appropriate Fish Bags and Packing Techniques
Selecting appropriate fish bags and packing techniques is crucial for successful transport․ Use high-quality, thick plastic bags designed for aquatic life, ensuring they are free from contaminants․ Fill bags with well-oxygenated water, creating enough space for fish to swim without overcrowding․ When sealing, ensure airtight closures to prevent leaks․ Additionally, utilize cushioning materials within insulated containers to protect against impacts during travel․ Properly label each container with species information and handling instructions․ Adopting these techniques enhances fish welfare, reduces stress, and increases survival rates during transportation․
6․2 Avoiding Overcrowding: The Key to Fish Health
Avoiding overcrowding during fish transport is essential for maintaining fish health and reducing stress․ When packing fish, adhere to recommended stocking densities to ensure adequate space for each individual․ Overcrowding can lead to increased aggression, competition for oxygen, and higher waste production, all of which negatively impact fish welfare․ Monitor the size and number of fish being packed, adjusting quantities based on species and size․ Providing sufficient room allows fish to swim freely, promotes better oxygenation, and ultimately enhances survival rates during transport, ensuring a healthier journey for aquatic life․
Stress Reduction Strategies for Fish
Implementing stress reduction strategies is vital for the successful transport of fish, promoting their health and welfare․ Begin by minimizing handling during the packing process, as excessive handling can elevate stress levels․ Use dim lighting to create a calming environment, as bright lights can startle fish․ Additionally, ensure that transport containers are stable and secure to prevent jolting during travel․ Providing adequate space and proper oxygenation helps maintain a serene environment․ By prioritizing stress reduction, you enhance fish welfare and increase the likelihood of survival during the journey․
7․1 Minimizing Handling Stress
Minimizing handling stress is crucial for the safe transport of fish, as excessive handling can significantly impact their health․ To achieve this, prepare all necessary equipment and materials in advance, reducing the time fish spend out of water․ Use nets that are soft and gentle to avoid injuring fish during capture․ When transferring fish, handle them with wet hands or gloves to protect their delicate skin․ Additionally, avoid sudden movements and loud noises, as these can startle fish․ By minimizing handling stress, you promote fish welfare and increase their chances of survival during transport․
7․2 Creating Comfortable Travel Conditions
Creating comfortable travel conditions is essential for ensuring fish welfare during transport․ Start by maintaining a stable water temperature within the ideal range for the specific species being transported․ Use insulated containers to minimize temperature fluctuations and protect fish from external elements․ Additionally, ensure that the transport environment is dark and quiet, reducing stress from sudden movements or loud noises․ Proper oxygenation is critical, so monitor levels throughout the journey․ By prioritizing these factors, you create a more comfortable environment that promotes fish health and increases survival rates during transport․
Fish Acclimation Post-Transport
Fish acclimation post-transport is a critical process that helps reduce stress and ensure a smooth transition to their new environment․ Upon arrival, begin by placing the sealed fish bags in the aquarium without opening them, allowing the fish to adjust to the temperature gradually․ After about 15-20 minutes, slowly introduce small amounts of tank water into the bags, gradually equalizing the water chemistry․ After another 15 minutes, gently transfer the fish into the aquarium using a net, avoiding the transfer of bag water․ This careful acclimation process promotes fish health and minimizes shock․
8;1 Importance of Acclimation to New Environments
Acclimation to new environments is essential for the successful integration of fish after transport․ This process helps fish adjust to changes in water temperature, chemistry, and overall habitat conditions, reducing the risk of shock and stress․ Sudden changes can lead to health issues, including lethargy or even death․ By allowing fish to acclimate gradually, you support their physiological adjustments and promote their well-being․ Fish that acclimate properly are more likely to thrive in their new environment, enhancing their chances of survival and overall health in the long run․
8․2 Steps for Proper Acclimation
Proper acclimation involves several critical steps to ensure fish adapt successfully to their new environment․ Begin by floating the sealed bags in the aquarium for 15-20 minutes to equalize the temperature․ Next, gradually introduce small amounts of aquarium water into the bags over the next 15-30 minutes, allowing fish to adjust to water chemistry changes․ After this period, use a net to transfer the fish into the tank, discarding the bag water to prevent contamination․ Monitor the fish closely for signs of stress and provide a quiet, low-light environment to facilitate acclimation․
Ensuring Fish Survival During Transport
Ensuring fish survival during transport is crucial for maintaining their health and well-being․ Begin by selecting appropriate containers that provide adequate space and insulation while ensuring proper oxygenation․ Monitor water temperature and oxygen levels regularly throughout the journey to prevent stress and discomfort․ Avoid overcrowding, as this can lead to increased competition for resources and higher mortality rates․ Additionally, minimize handling and create a calm environment to reduce stressors․ By prioritizing these factors, you significantly enhance fish survival rates during transport and contribute to their overall well-being․
9․1 Recognizing Signs of Stress and Distress
Recognizing signs of stress and distress in fish during transport is vital for ensuring their well-being․ Common indicators include rapid gill movement, erratic swimming patterns, and excessive hiding or lethargy․ Additionally, fish may display color changes, such as fading or darkening, which signal stress levels․ Observe for signs of gasping at the water surface, indicating potential oxygen depletion․ If fish are excessively bumping against the walls of their containers, this may also suggest discomfort․ Being vigilant about these signs can help address issues promptly, improving survival chances during transport․
9․2 Tips for Maintaining Fish Welfare
Maintaining fish welfare during transport is essential for their health and survival․ Begin by ensuring that transport containers are clean and appropriate for the species being moved․ Provide adequate space to prevent overcrowding, which can lead to stress․ Regularly monitor water temperature and oxygen levels, adjusting as necessary to create optimal conditions․ Avoid sudden movements and loud noises, as these can startle fish․ Additionally, feed fish lightly before transport to minimize waste․ By applying these tips, you can significantly enhance fish welfare and increase their chances of thriving post-transport․
Transporting fish requires careful attention to various factors to ensure their health and survival․ Begin by selecting appropriate containers, ensuring proper water quality and oxygen levels․ Monitor temperature throughout the journey, and implement stress reduction strategies to minimize discomfort․ Use efficient acclimation techniques upon arrival to aid fish adaptation․ Recognizing signs of stress and maintaining fish welfare during transport are crucial for success․ By following these best practices, you enhance the likelihood of successful transport, promoting the well-being of aquatic life and ensuring a smooth transition to new environments․













Post Comment